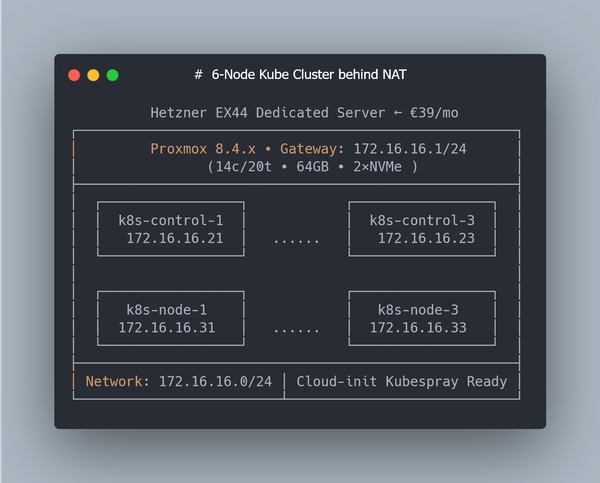
How to Create a Proxmox User, Role and API Token for Terraform
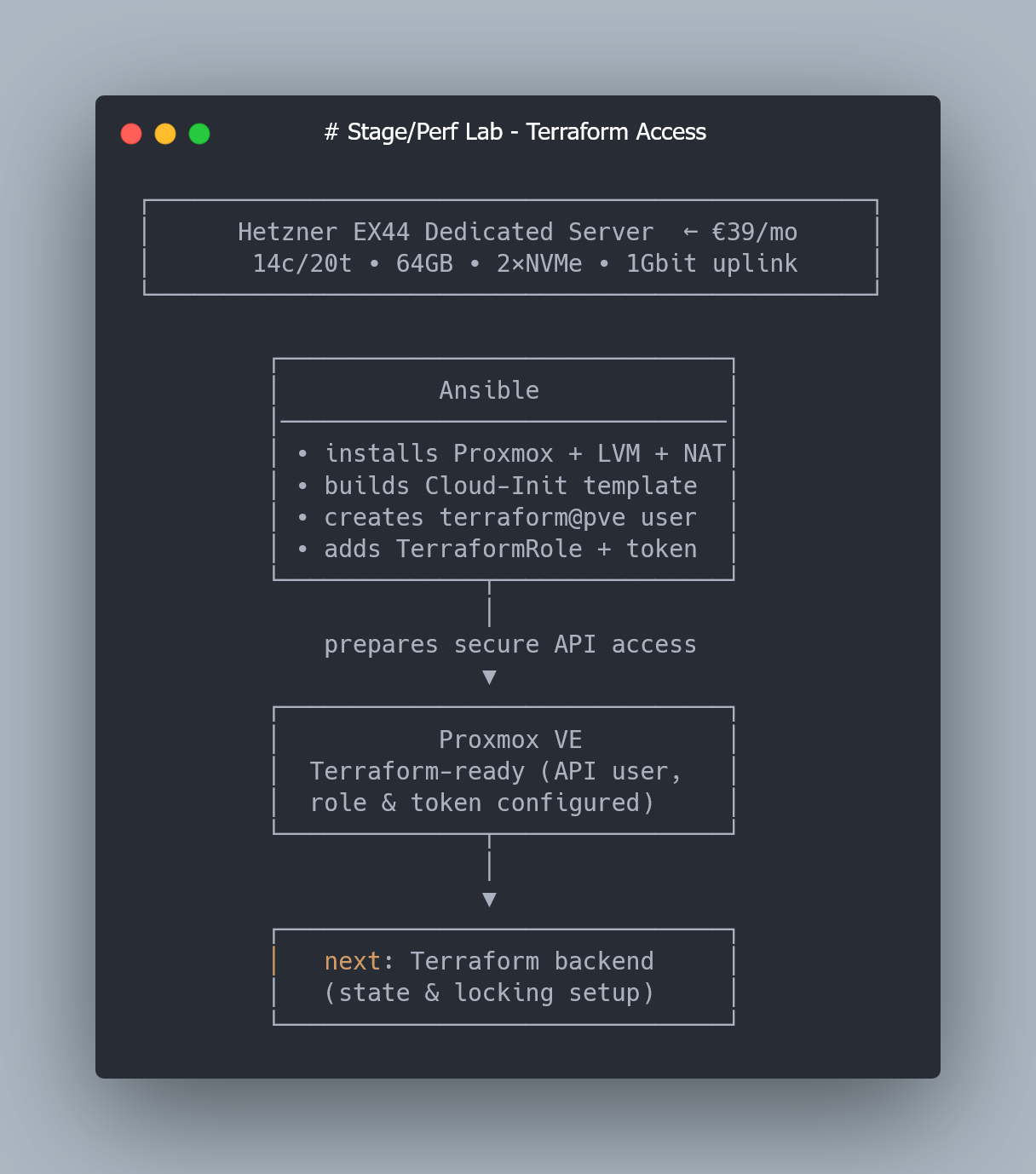
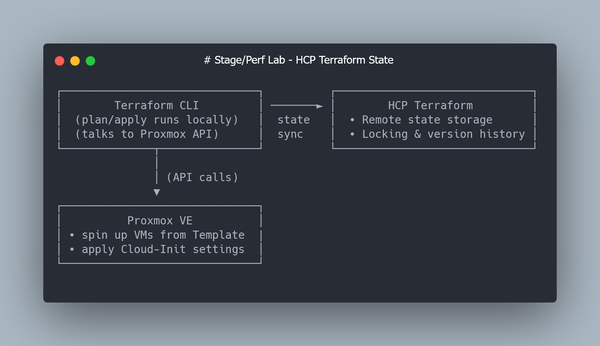
Terraform interacts with Proxmox over the API.
For security (and reproducibility), it’s better to create a dedicated user with a token, instead of reusing your root account.
We’ll create:
- a new user terraform@pve
- an API token (terraform-token)
- a custom role TerraformRole with the all permissions required for bpg Terraform provider.
ℹ️ Note on authentication realms: pam vs pve
In Proxmox each user belongs to an authentication realm. The two most common are:
- pam — system-level Linux users from
/etc/passwd.
If you createterraform@pam, it will be a normal Linux user with access to the Proxmox API using a password. - pve — internal Proxmox realm stored in
/etc/pve.
These users exist only inside Proxmox and cannot log into the host system.
This realm is ideal for service accounts and API tokens, because it keeps them isolated from system-level accounts.
In this guide we’ll use terraform@pve, because:
- it separates API users from system users,
- it works seamlessly with API tokens (no passwords),
- and it allows fine-grained role-based access control.
Proxmox Terraform Role Permissions (Working Config for bpg/proxmox Provider)
Run this command on the Proxmox host to create a role with required permissions:
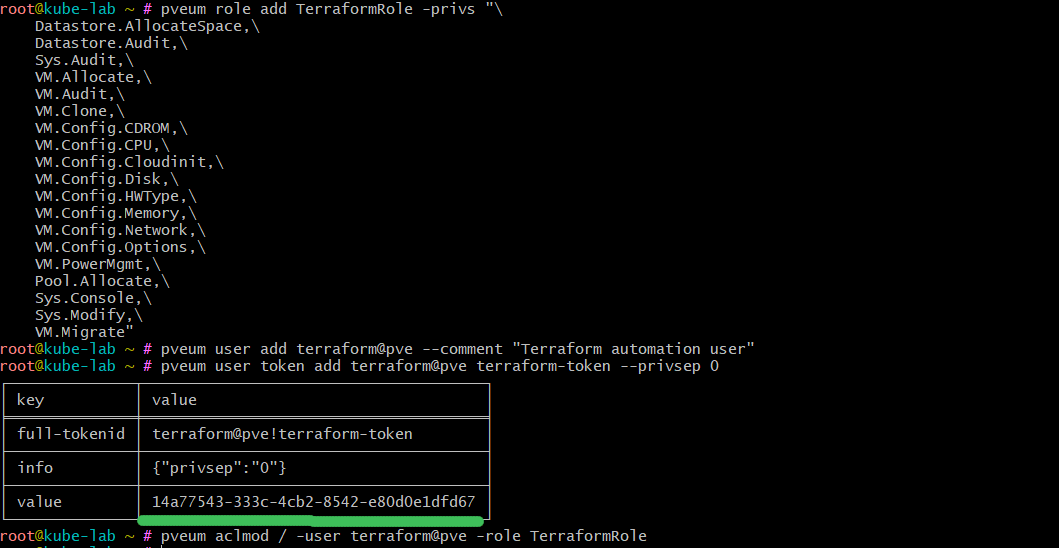
pveum role add TerraformRole -privs "\
Datastore.Allocate,\
Datastore.AllocateSpace,\
Datastore.Audit,\
Sys.Audit,\
Sys.Modify,\
Sys.PowerMgmt,\
VM.Allocate,\
VM.Audit,\
VM.Clone,\
VM.Config.CDROM,\
VM.Config.Cloudinit,\
VM.Config.CPU,\
VM.Config.Disk,\
VM.Config.HWType,\
VM.Config.Memory,\
VM.Config.Network,\
VM.Config.Options,\
VM.Migrate,\
VM.Monitor,\
VM.PowerMgmt,\
SDN.Use"
Permission breakdown (for bpg/proxmox):
- Datastore.Allocate, Datastore.AllocateSpace — allow Terraform to create and resize VM disks.
- Datastore.Audit — list available storages (needed for cloning).
- Sys.Audit, Sys.Modify, Sys.PowerMgmt — read system info, modify basic settings, manage power actions.
- VM.Allocate, VM.Audit — create new VMs, list/read VM configuration.
- VM.Clone — clone from a template (our golden image).
- VM.Config.* — full configuration management: attach Cloud-Init, set CPU, memory, disks, NICs, machine type, modify VM metadata (boot order, name, tags).
- VM.Migrate — allow live or cold migration.
- VM.Monitor — monitor VM state (required for bpg provider).
- VM.PowerMgmt — start, stop, reboot VMs.
- SDN.Use — required if you use Proxmox SDN / bridges with bpg provider.
Create a dedicated user
pveum user add terraform@pve --comment "Terraform automation user"
3.3 Create an API token
pveum user token add terraform@pve terraform-token --privsep 0
--privsep 0disables privilege separation, so the token inherits all rights of its user (in our case only the minimal for TerraformRole we assigned).
This will output a token ID and a secret.
⚠️ Save them carefully — the secret is shown only once.
3.4 Assign the role to the user
pveum aclmod / -user terraform@pve -role TerraformRole
This binds our custom role to the entire Proxmox cluster (/).
Terraform can now use the API to create and manage VMs, but nothing more.
✅ With this setup you now have a dedicated Terraform account that can safely spin up VMs using your golden template.